Learn Chymotrypsin’s Catalytic Mechanism with free step-by-step video explanations and practice problems by experienced tutors. … Theus Elation phase can really be broken down into these four general steps, which are listed down below. And they are substrate binding nuclear filic attack, removal of leaving group or the LG for short and end of
SOLVED: What do you need to know? On the figure below that shows the catalytic steps employed by chymotrypsin a) label the amino acids in the catalytic triad b) label the catalytic
This conforms exactly to the mechanism described above.; For chymotrypsin-catalyzed cleavage, the step characterized by \(k_2\) is the acylation step (with release of the leaving group such as p-nitrophenol in Lab 5). The step characterized by \(k_3\) is the deacylation step in which water attacks the acyl enzyme to release product \(P\).
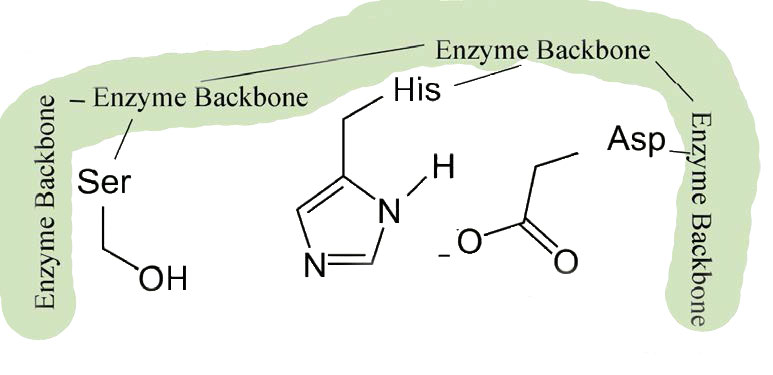
Source Image: openoregon.pressbooks.pub
Download Image
The enzyme’s action occurs in two phases – a fast phase that occurs first and a slower phase that follows. The enzyme has a substrate binding site that includes a region of the enzyme known as the S1 pocket. Let us step through the mechanism by which chymotrypsin cuts adjacent to phenylalanine. Figure 6.2.1: Serine protease mechanism.

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
3.3: Mechanisms of Catalysis – Introductory Biochemistry
To do this, the tRNA molecules must first be attached to the appropriate amino acid. Specific enzymes are available called amino acyl – tRNA synthetases that mediate this reaction. The synthetase enzymes use the energy of ATP to covalently attach the amino acid to the tRNA molecule. Chapter 7: Catalytic Mechanisms of Enzymes.

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
Put These Steps In The Mechanism Of Chymotrypsin Catalysis
To do this, the tRNA molecules must first be attached to the appropriate amino acid. Specific enzymes are available called amino acyl – tRNA synthetases that mediate this reaction. The synthetase enzymes use the energy of ATP to covalently attach the amino acid to the tRNA molecule. Chapter 7: Catalytic Mechanisms of Enzymes.
Aug 31, 20234.7: Chymotrypsin. Consider the mechanism of catalysis of the enzyme known as chymotrypsin. Found in our digestive system, chymotrypsin’s catalytic action is cleaving peptide bonds in proteins and it uses the side chain of a serine in its mechanism of catalysis. Many other protein- cutting enzymes employ a very similar mechanism and they are
Chymotrypsin Mechanism Flashcards | Quizlet
Feb 13, 2023Introduction. Chymotrypsin is one of the most studied enzymes due to its two phase kinetics: pre-steady-state and steady state. The study of these two kinetic states gives evidence of the “Ping-Pong” mechanism, the formation of covalent complexes leading to covalent hydrolysis reactions, and the rate of the catalyzed reactions.
Biochemistry I – Chapter 9 Flashcards | Quizlet

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Enzyme mechanism: Chymotrypsin catalyzes hydrolysis of proteins at specific peptide bonds of aromatic amino acid residues. There are four general principles of enzyme catalysis. What two principles are utilized by chymotrypsin?
Feb 13, 2023Introduction. Chymotrypsin is one of the most studied enzymes due to its two phase kinetics: pre-steady-state and steady state. The study of these two kinetic states gives evidence of the “Ping-Pong” mechanism, the formation of covalent complexes leading to covalent hydrolysis reactions, and the rate of the catalyzed reactions.
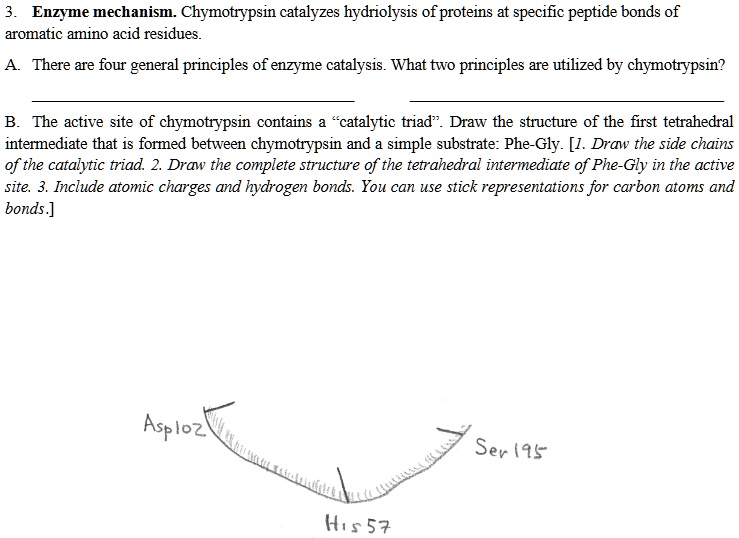
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
SOLVED: What do you need to know? On the figure below that shows the catalytic steps employed by chymotrypsin a) label the amino acids in the catalytic triad b) label the catalytic
Learn Chymotrypsin’s Catalytic Mechanism with free step-by-step video explanations and practice problems by experienced tutors. … Theus Elation phase can really be broken down into these four general steps, which are listed down below. And they are substrate binding nuclear filic attack, removal of leaving group or the LG for short and end of
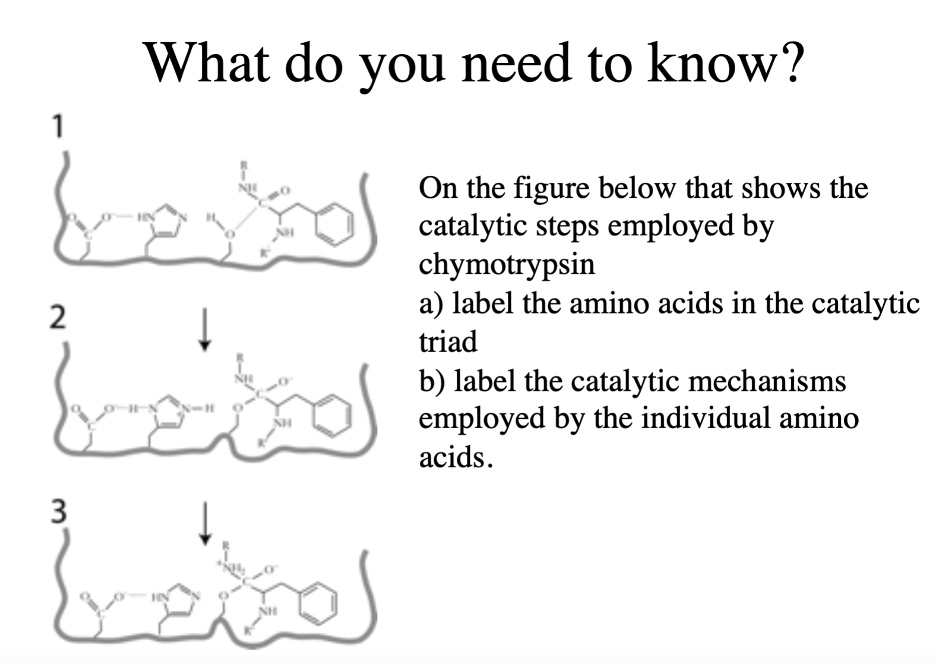
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
3.3: Mechanisms of Catalysis – Introductory Biochemistry
The enzyme’s action occurs in two phases – a fast phase that occurs first and a slower phase that follows. The enzyme has a substrate binding site that includes a region of the enzyme known as the S1 pocket. Let us step through the mechanism by which chymotrypsin cuts adjacent to phenylalanine. Figure 6.2.1: Serine protease mechanism.
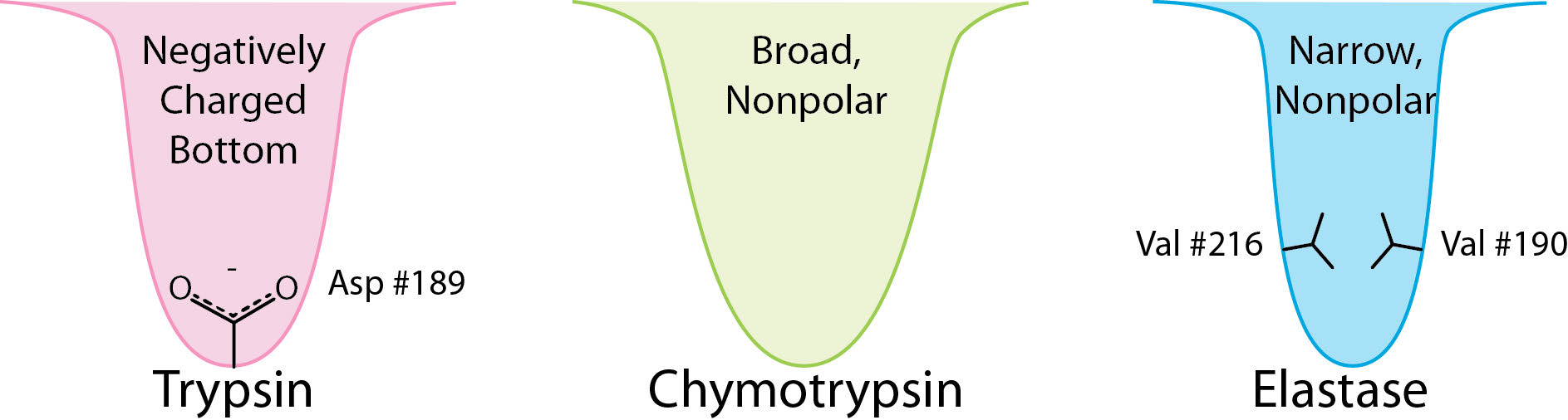
Source Image: openoregon.pressbooks.pub
Download Image
Chymotrypsin – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Nov 1, 2023Chymotrypsin, a protease, is an enzyme that cleaves the carbonyl side of certain peptide bonds by both general acid-base catalysis, but primarily covalent catalysis. In this mechanism, a nucleophile becomes covalently attached to a substrate in a transition state with an acyl-enzyme.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Mechanism of Chymotrypsin Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Peptide Bond
To do this, the tRNA molecules must first be attached to the appropriate amino acid. Specific enzymes are available called amino acyl – tRNA synthetases that mediate this reaction. The synthetase enzymes use the energy of ATP to covalently attach the amino acid to the tRNA molecule. Chapter 7: Catalytic Mechanisms of Enzymes.
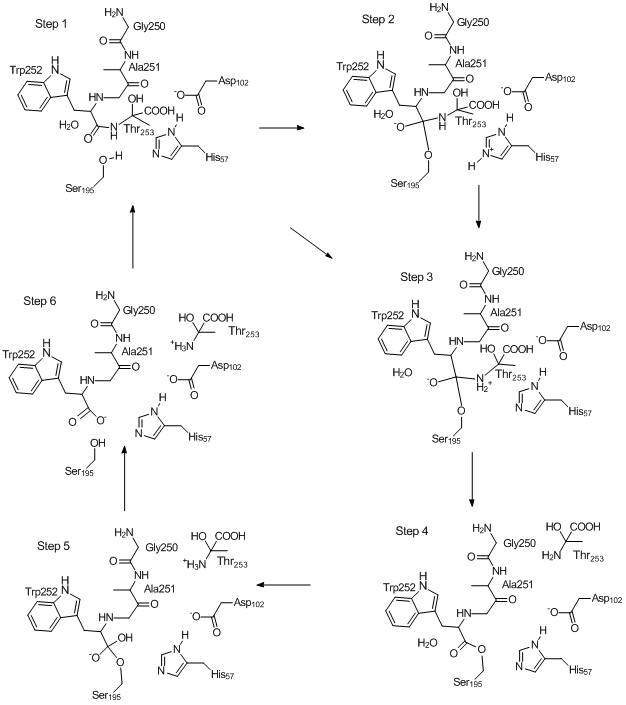
Source Image: openmopac.net
Download Image
Chymotrypsin – Mechanism of action – YouTube
Aug 31, 20234.7: Chymotrypsin. Consider the mechanism of catalysis of the enzyme known as chymotrypsin. Found in our digestive system, chymotrypsin’s catalytic action is cleaving peptide bonds in proteins and it uses the side chain of a serine in its mechanism of catalysis. Many other protein- cutting enzymes employ a very similar mechanism and they are

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Enzyme mechanism: Chymotrypsin catalyzes hydrolysis of proteins at specific peptide bonds of aromatic amino acid residues. There are four general principles of enzyme catalysis. What two principles are utilized by chymotrypsin?
Chymotrypsin – Mechanism of action – YouTube
This conforms exactly to the mechanism described above.; For chymotrypsin-catalyzed cleavage, the step characterized by \(k_2\) is the acylation step (with release of the leaving group such as p-nitrophenol in Lab 5). The step characterized by \(k_3\) is the deacylation step in which water attacks the acyl enzyme to release product \(P\).
3.3: Mechanisms of Catalysis – Introductory Biochemistry Mechanism of Chymotrypsin Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Peptide Bond
Nov 1, 2023Chymotrypsin, a protease, is an enzyme that cleaves the carbonyl side of certain peptide bonds by both general acid-base catalysis, but primarily covalent catalysis. In this mechanism, a nucleophile becomes covalently attached to a substrate in a transition state with an acyl-enzyme.