4 days agoupdated: January 19, 2024 Definition 00:00 00:26 Mitosis is the process by which a cell replicates its chromosomes and then segregates them, producing two identical nuclei in preparation for cell division. Mitosis is generally followed by equal division of the cell’s content into two daughter cells that have identical genomes. Mitosis 3-D
What is Mitosis? | Let’s Talk Science
Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. This process is essential for growth and repair in the body. On the other hand, meiosis occurs in germ cells and produces four non-identical gametes with a haploid (n) number of chromosomes.
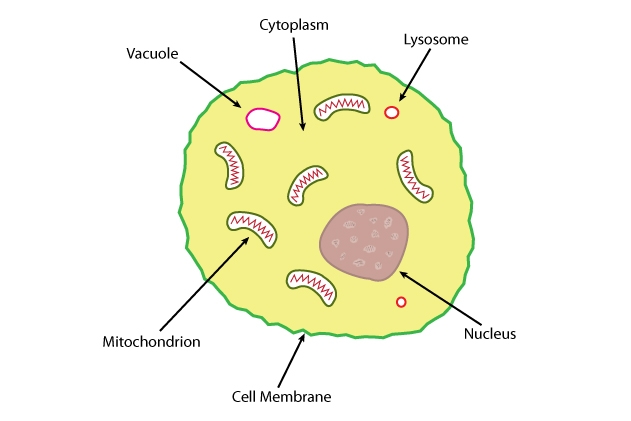
Source Image: sciencelearn.org.nz
Download Image
During mitosis, the cell division part of the cell cycle, a single parent cell’s replicated genetic material—called chromosomes—divides to produce two new, genetically-identical daughter cells. In the cell cycle, the cell’s DNA is replicated in interphase, the phase that precedes mitosis.
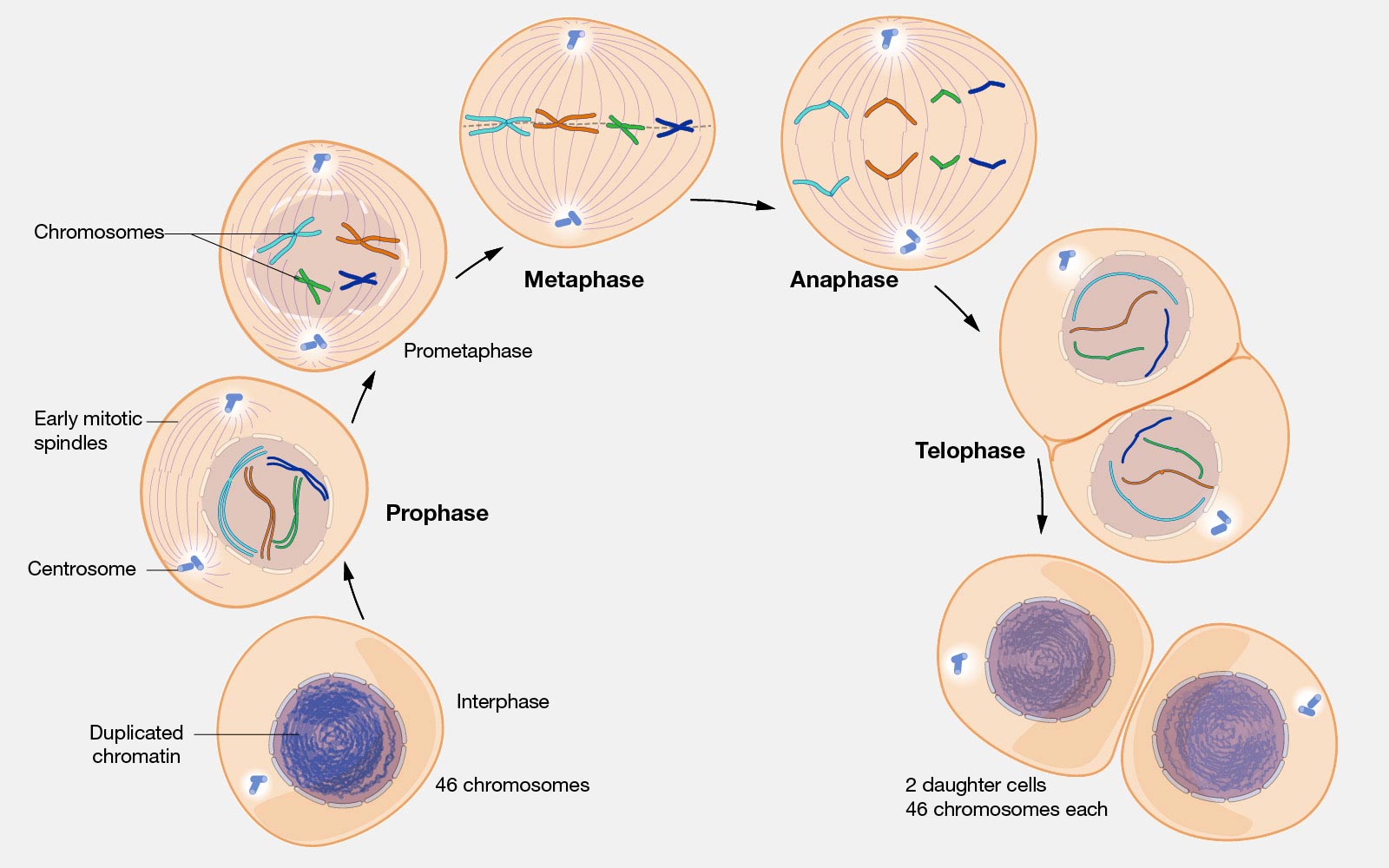
Source Image: scitechdaily.com
Download Image
Cell Division – Mitosis and Meiosis | Ask A Biologist Mitosis ( / maɪˈtoʊsɪs /) is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained.
(69).jpg)
Source Image: proprofs.com
Download Image
Mitosis Produces Only What Type Of Cells
Mitosis ( / maɪˈtoʊsɪs /) is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Mitosis is the step in the cell cycle that the newly duplicated DNA is separated, and two new cells are formed. This process is important in single-celled eukaryotes, as it is the process of asexual reproduction. In multi-celled eukaryotes, mitosis is how a single zygote can become an entire organism.
Biology: Cell Division Quiz On Mitosis And Meiosis! – Trivia & Questions
Jan 3, 2024mitosis, a process of cell duplication, or reproduction, during which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells. Strictly applied, the term mitosis is used to describe the duplication and distribution of chromosomes, the structures that carry the genetic information. A brief treatment of mitosis follows. The cell: Types, functions, and organelles

Source Image: medicalnewstoday.com
Download Image
10 Key Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis | Mitosis, Meiosis, Mitosis vs meiosis Jan 3, 2024mitosis, a process of cell duplication, or reproduction, during which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells. Strictly applied, the term mitosis is used to describe the duplication and distribution of chromosomes, the structures that carry the genetic information. A brief treatment of mitosis follows.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
What is Mitosis? | Let’s Talk Science 4 days agoupdated: January 19, 2024 Definition 00:00 00:26 Mitosis is the process by which a cell replicates its chromosomes and then segregates them, producing two identical nuclei in preparation for cell division. Mitosis is generally followed by equal division of the cell’s content into two daughter cells that have identical genomes. Mitosis 3-D
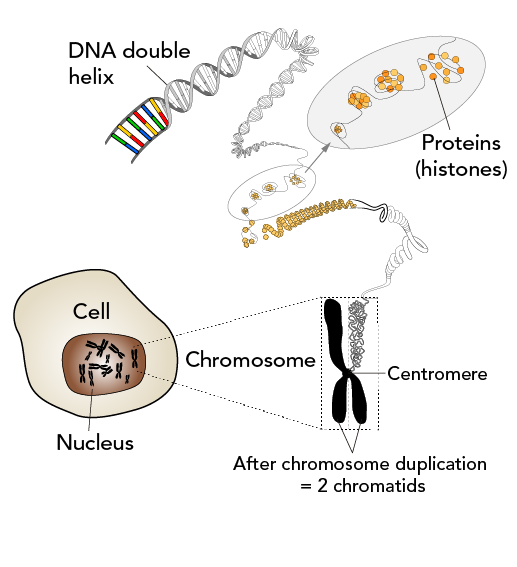
Source Image: letstalkscience.ca
Download Image
Cell Division – Mitosis and Meiosis | Ask A Biologist During mitosis, the cell division part of the cell cycle, a single parent cell’s replicated genetic material—called chromosomes—divides to produce two new, genetically-identical daughter cells. In the cell cycle, the cell’s DNA is replicated in interphase, the phase that precedes mitosis.
Source Image: askabiologist.asu.edu
Download Image
Mitosis in Onion Root Tips — DataClassroom Course: MCAT > Unit 6 Test prep > MCAT > Foundation 2: Cells > Cellular division Mitosis Google Classroom You started off as a fertilized cell inside your mom, called a zygote. Now, you’re a thriving community of hundreds of millions of cells, all working together towards a common purpose: to keep you alive.
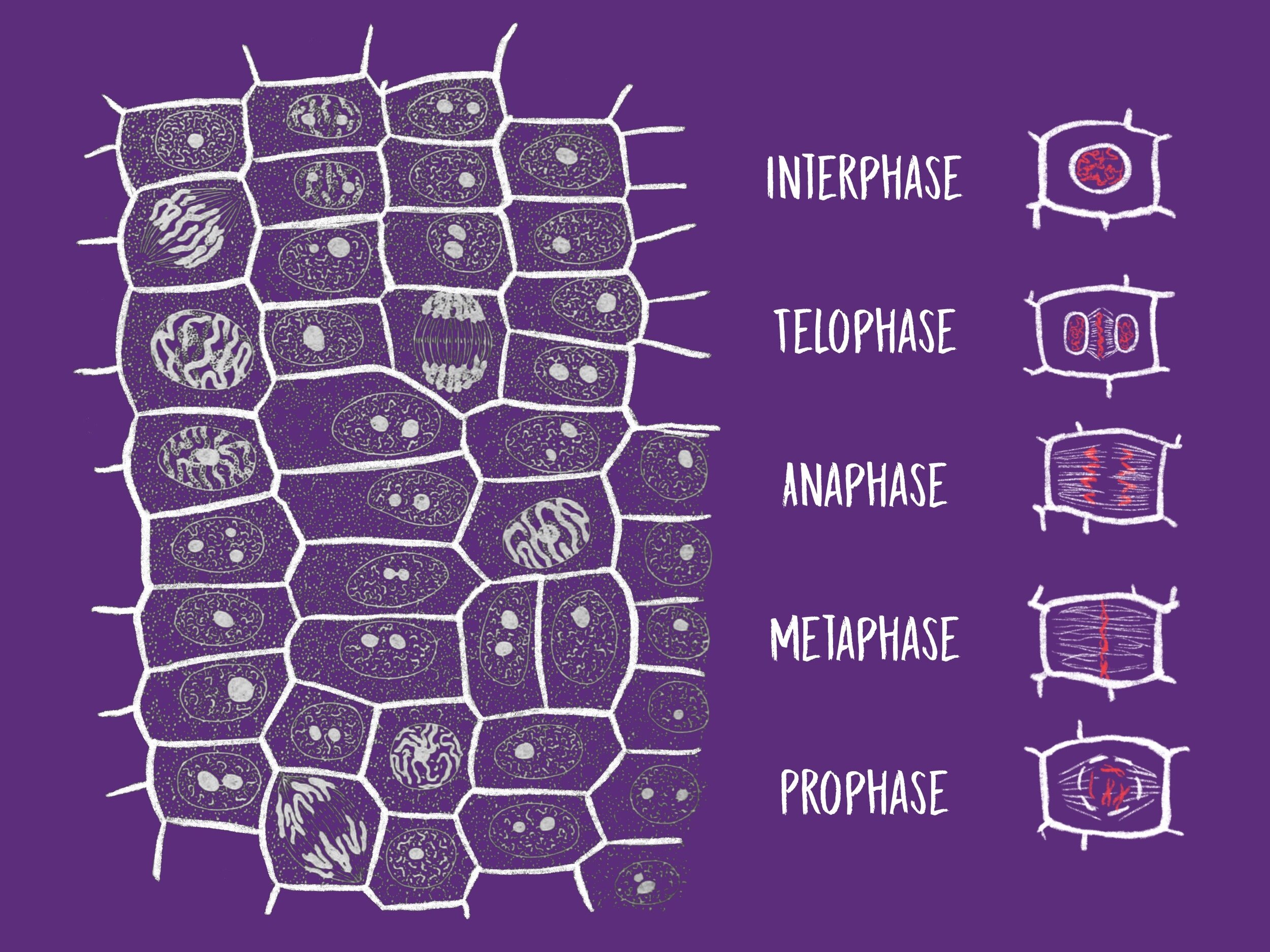
Source Image: about.dataclassroom.com
Download Image
Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology – Nurseslabs Mitosis ( / maɪˈtoʊsɪs /) is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained.
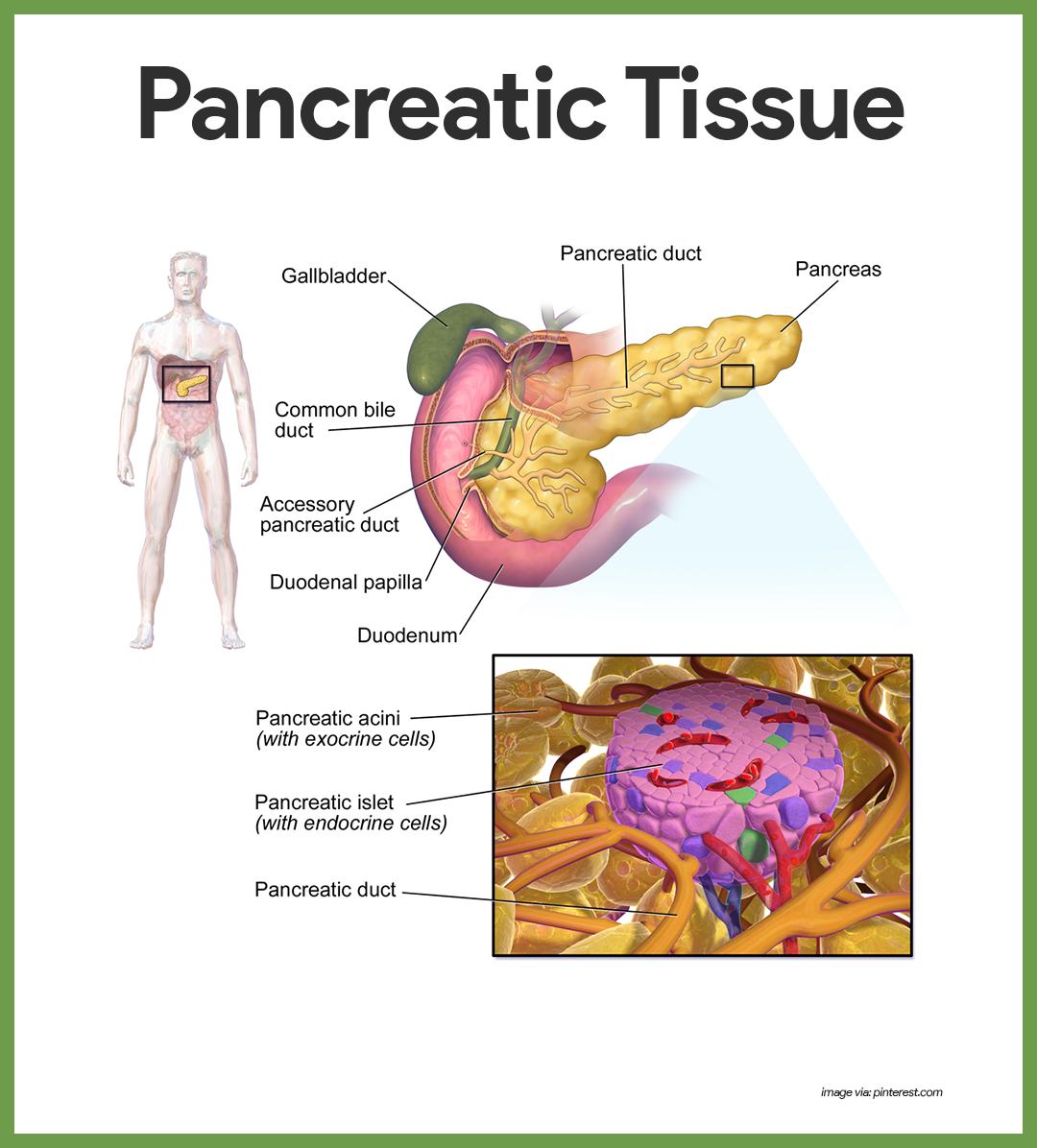
Source Image: nurseslabs.com
Download Image
DNA, Mutations And Mitosis Quiz – Trivia & Questions Mitosis is the step in the cell cycle that the newly duplicated DNA is separated, and two new cells are formed. This process is important in single-celled eukaryotes, as it is the process of asexual reproduction. In multi-celled eukaryotes, mitosis is how a single zygote can become an entire organism.

Source Image: proprofs.com
Download Image
10 Key Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis | Mitosis, Meiosis, Mitosis vs meiosis
DNA, Mutations And Mitosis Quiz – Trivia & Questions Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. This process is essential for growth and repair in the body. On the other hand, meiosis occurs in germ cells and produces four non-identical gametes with a haploid (n) number of chromosomes.
Cell Division – Mitosis and Meiosis | Ask A Biologist Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology – Nurseslabs Course: MCAT > Unit 6 Test prep > MCAT > Foundation 2: Cells > Cellular division Mitosis Google Classroom You started off as a fertilized cell inside your mom, called a zygote. Now, you’re a thriving community of hundreds of millions of cells, all working together towards a common purpose: to keep you alive.